- Where do rivers get their water from?
- When do rivers have a lot of water?
- What causes the water level to change in rivers?
Where do rivers get their water from?
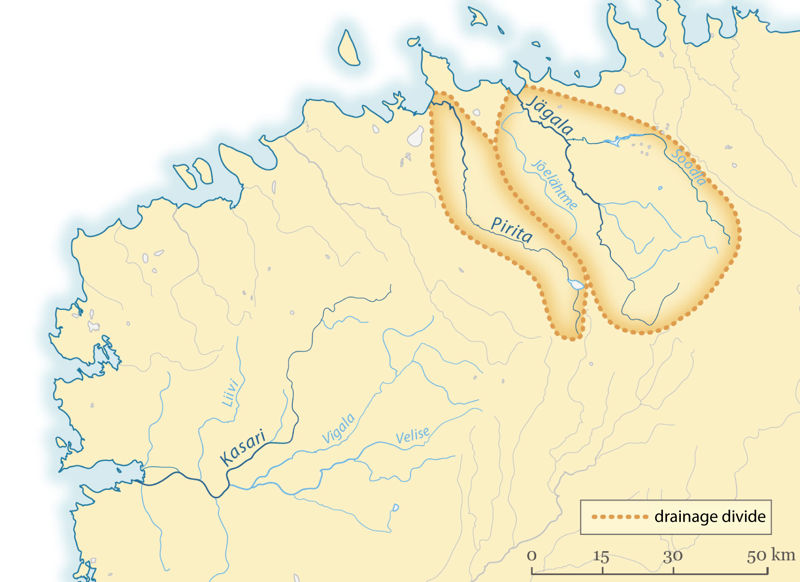
Rivers get their water from rain, snowmelt, and springs. The water level fluctuates based on the seasons and weather conditions. Some of the rainwater infiltrates the ground, some evaporates in the sun, and some of it flows along the slope of the ground until it reaches a body of water. The water that flows into a common body of water, such as a river, comes from a place called a drainage basin. The larger the basin, the more small streams and rivers flow from it, the more water the mainstem receives. Drainage basins are essentially a type of water collecting area, and the places that collect water are called catchment areas. The catchment areas of neighbouring rivers are separated by higher ground that water has to flow around. These higher places are called drainage divides.
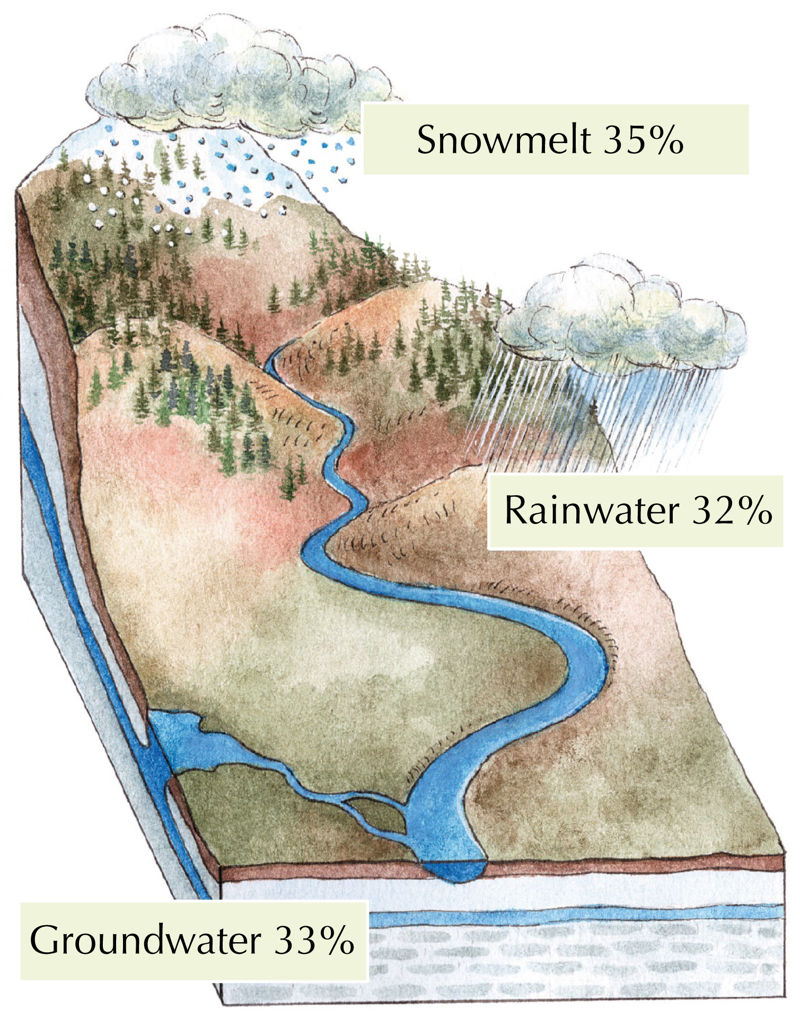
When is there the most water in a river?
In autumn or winter, when the river becomes covered in ice, precipitation can not affect the water level anymore. The water level is low because the river flowing under the ice cover feeds only on the groundwater that reaches the river through the springs.
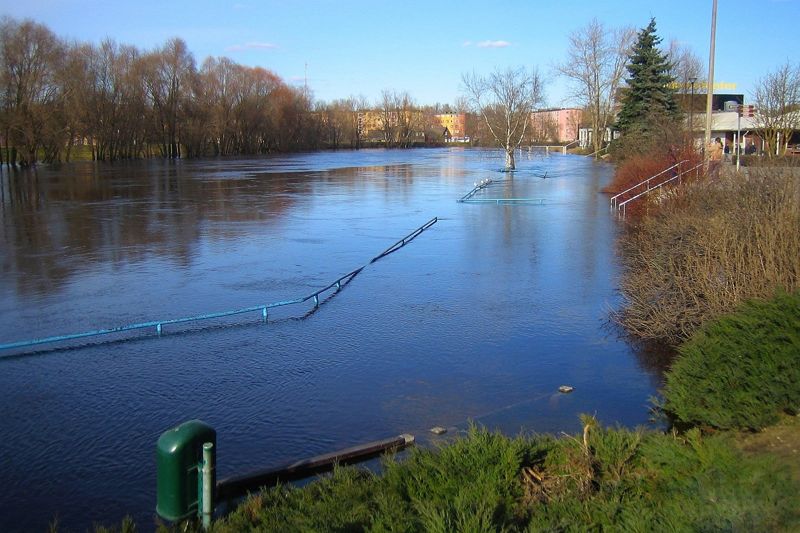
When the sun rises higher in spring, the ice melts and breaks into pieces, and the flowing water carries the pieces away. The river is now free from the ice cover. With the onset of spring, the high water occurs as the water level rises, turning small streams into wide rivers. Often, the riverbed cannot hold the sudden large amounts of snowmelt that flows into the river in spring. The water floods the banks, and may even cover the whole river valley – meadows, forests, sometimes even city streets. Floods are common on the wide slow-flowing rivers of the plains.
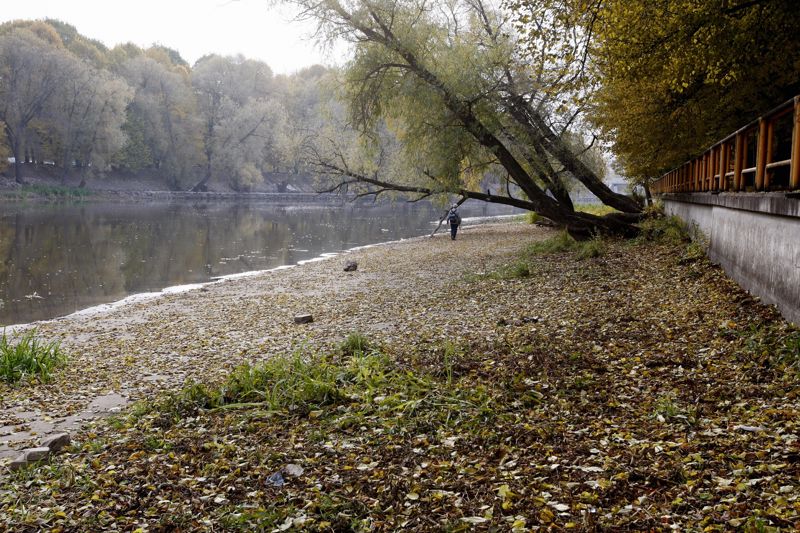
In hot, dry summers, the water level in a river can often get so low that the hills of rocks and sand at the bottom of the riverbed become visible above the water's surface. This phenomenon is called low water, or baseflow. Water levels will rise again in late summer and autumn as rainfall increases. Have you noticed that it is raining the most in August, September and October? However, the high water in autumn is usually still lower than in spring.
Bonus: The river discharge
The more deep and wide the river, the more water can flow in it – the bigger the discharge of the river. The discharge of the river indicates how much water flows through a cross-section of a river bed (eg. the river mouth) in one unit of time (eg. in a second, day or year). In what season would you expect the discharge to be the biggest?
Think!
- Where do the largest rivers in the world get their water from? When are these rivers water-rich, when are they water-poor?
Important terms
- high water – the water level rise in bodies of water, often accompanied with floods
- baseflow – the low water level that occurs when there is no precipitation or snowmelt, and the river feeds mostly on groundwater
- drainage basin – the area from which the water that flows into a common body of water comes from, bordered by a drainage divide
- drainage divide – an elevated area that separates the neighboring drainage basins
I now know that…
Rivers can get their water from snowmelt, precipitation, or groundwater. The area from which water accumulates in a river is called a drainage basin. In spring, rivers have high water due to the snowmelt that flows into rivers, and in summer they have low water.


