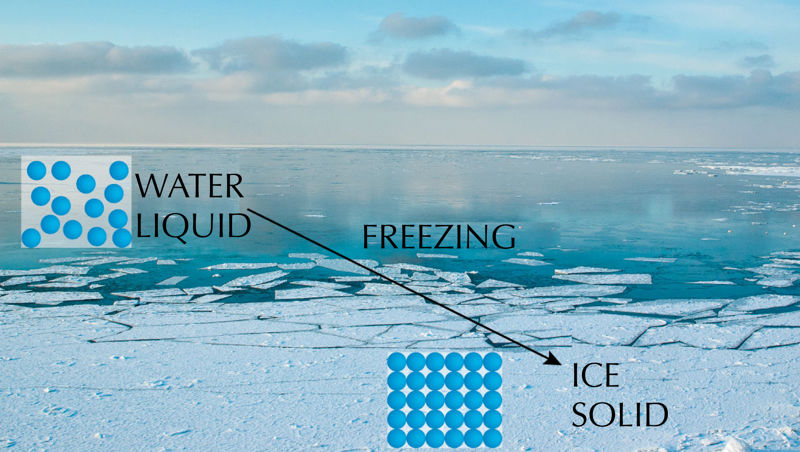
The three states of water
Water occurs in nature as ice or snow, liquid water, or water vapour, which are each in a solid, liquid, or gaseous state. The state of matter is the form that the substance can take. In different states of matter, the arrangement of the particles and their relationships are different, but the substance itself remains the same. Liquid water, water vapour, and ice are all made of water molecules - H2O.

Melting and freezing
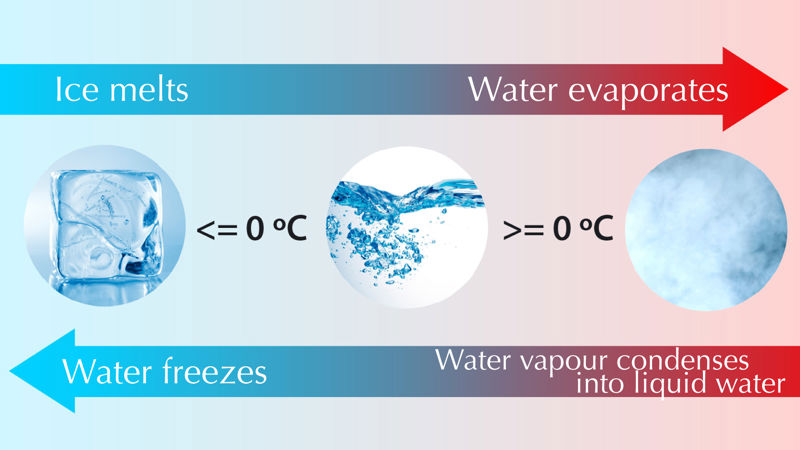
At 0°C, the state of the water begins to change - the liquid water turns to ice. The change from a liquid state to a solid state is called freezing, and solid substances are called solids.
If you put an ice cube in a glass in a warm room, it will start to melt immediately. A solid melts and becomes a liquid.
- Light
- Temperature
- Moon phase
Evaporation and condensation
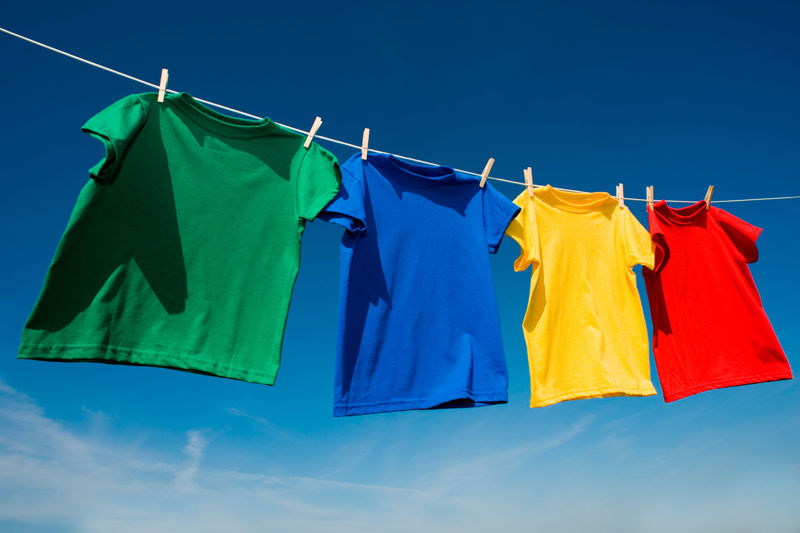
If you hang wet laundry to dry, it will dry after a while. This is due to evaporation: water becomes water vapour and disperses into the air. The warmer the air and the windier the weather, the faster the evaporation. The state of water changes as the liquid substance becomes a gas. Water can also change its state from a solid to a gas without turning into a liquid in-between. This happens, for example, when you take your laundry to dry outside in cold weather in winter.
At 100°C, the water starts to boil, and at this temperature, the water evaporates quickly. As the air above the pot is much cooler, the water vapour cools and condenses, meaning that it becomes water droplets. As it condenses, the state of the water changes, the gaseous substance becomes a liquid substance. For the same reason, a mirror or glass becomes hazy when you breathe on it, because when your breath comes in contact with the surface of a cold mirror, it cools, and the water vapour in it condenses into water. Remember that we do not see water vapour. What we see is actually condensed water vapour, or liquid water.
Think!
- Give examples of where on Earth we can find water in a liquid state, where in a gaseous state, and where in a solid state.
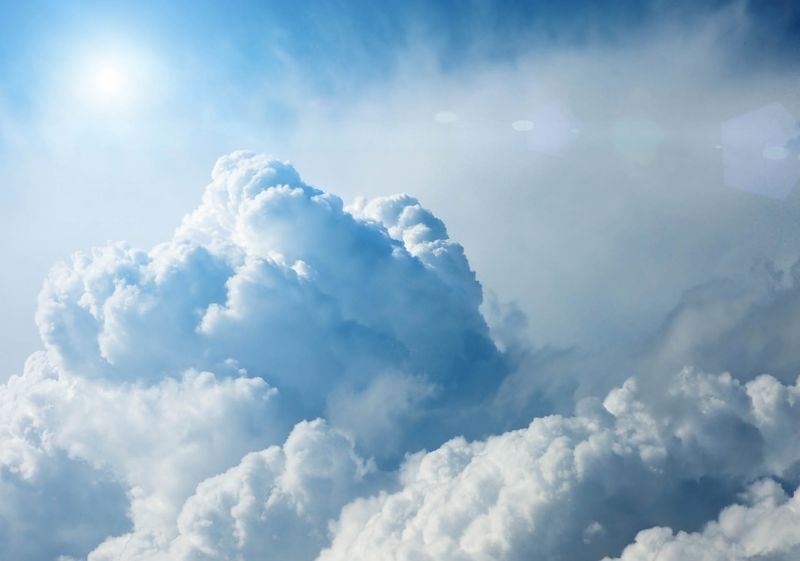
Bonus: How do clouds form?
Water is constantly evaporating from the surface of bodies of water and the ground. Warm air begins to rise, where the air is cool, and water vapour condenses into tiny droplets. Clusters of small water droplets become visible as a cloud. As the droplets join together, the cloud thickens. When the condensed droplets become too large and so heavy that they can no longer stay in the air, they fall again as rain.

Important terms
- solid – a substance in a solid state
- liquid – a substance in a liquid state
- gas – a substance in a gaseous state
- evaporation – the change of a liquid into a gas
- melting – the change of a solid into a liquid
- freezing – the change of a liquid into a solid
- condensation – the change of a gas into a liquid
I now know that…
Water is found in nature in three states: solid, gaseous, and liquid. In the solid state, water is ice; in the liquid state, it is a liquid; and in the gaseous state, water is water vapour.